Introduction
Three Winding Transformer in Power Systems
Three Winding Transformer is specialized transforme that features three separate windings: one primary winding and two secondary windings. This design enables them to provide multiple voltage outputs from a single input. The ability to supply different voltage levels from one transformer makes them invaluable in complex power systems where various components require different voltages.
The significance of Three Winding Transformers lies in their enhanced voltage regulation and load balancing capabilities. They help stabilize power distribution by efficiently managing multiple voltage levels, which is crucial for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of electrical networks. By reducing harmonic distortions and improving voltage control, Three Winding Transformers contribute to the overall performance and safety of power systems, making them an essential component in modern electrical infrastructure.
What is a Three Winding Transformer?
Definition and Basic Concept
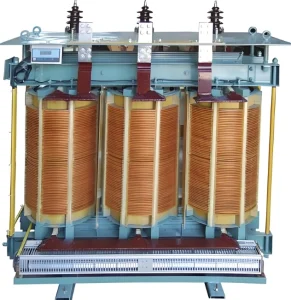
A Three Winding Transformer is a type of transformer that features three distinct windings: one primary winding and two secondary windings. It is designed to transfer electrical energy between circuits while providing multiple voltage outputs from a single input. This configuration allows it to handle various voltage levels efficiently, making it ideal for complex power systems.
Comparison with Two-Winding Transformers
Compared to two-winding transformers, Three Winding Transformers offer greater versatility. Two-winding transformers have one primary and one secondary winding, which limits them to a single voltage transformation. In contrast, the three-winding design allows for multiple voltage levels. This additional flexibility is particularly useful in applications where different voltages are required for different parts of the system.
Moreover, Three Winding Transformers improve load balancing and voltage regulation. They can manage multiple loads more effectively and provide better performance in situations where power needs to be distributed among various circuits. This makes them more suitable for large-scale power distribution networks compared to their two-winding counterparts.
Key Components and Structure
The primary components of a Three Winding Transformer include the primary winding, two secondary windings, and the core.
- Primary Winding: This is the input winding that receives electrical energy from the power source.
- Secondary Windings: These are the output windings that deliver different voltage levels to various parts of the system.
- Core: The core is made of laminated steel sheets to reduce energy losses. It provides a pathway for the magnetic flux created by the windings.
The windings are usually made of copper or aluminum and are insulated to prevent electrical shorts. The core and windings are housed in a robust casing that protects them from environmental factors and mechanical damage.
In summary, the three-winding design enhances the transformer’s ability to manage different voltage levels and improve overall system efficiency.
Applications of Three Winding Transformer
Utility and Industrial Applications
Three Winding Transformers are extensively used in both utility and industrial applications. In utility settings, they are vital for managing and distributing electrical power across different regions. These transformers help in connecting various parts of the power grid, ensuring that different voltage levels are efficiently supplied to residential, commercial, and industrial users.
In industrial environments, Three Winding Transformers are employed to support complex machinery and equipment that operate at different voltage levels. They provide the necessary voltage adjustments to ensure smooth and reliable operation of industrial processes. This capability is crucial for facilities with diverse electrical demands, such as manufacturing plants and large-scale processing units.
Role in Power Distribution Systems
In power distribution systems, Three Winding Transformers play a key role in distributing electrical power from high voltage transmission lines to lower voltage distribution networks. They are used at substations to step down the high transmission voltage to levels suitable for local distribution. This process ensures that power is delivered efficiently and safely to end-users.
Additionally, Three Winding Transformers facilitate the interconnection of different voltage levels within the power grid. They help balance loads and ensure that power is evenly distributed across various circuits, which improves the stability and reliability of the power system.
Use in Voltage Regulation and Load Balancing
Three Winding Transformers are particularly effective in voltage regulation and load balancing. They can provide multiple voltage outputs from a single input, which allows for precise control of voltage levels across different parts of the power system. This capability is essential for maintaining stable voltage levels and preventing fluctuations that can impact electrical equipment and system performance.
Load balancing is another critical function of Three Winding Transformers. By distributing power across multiple circuits and adjusting voltage levels, these transformers help ensure that no single part of the system is overloaded. This balance prevents potential issues such as overheating and ensures that the electrical network operates efficiently and safely.
Types of Three Winding Transformer
Power transformers are the most prevalent type of Three Winding Transformers used in high-voltage power transmission and distribution systems. They are specifically engineered to manage substantial amounts of electrical power and are commonly located in substations. By handling high voltage levels, power transformers ensure stable voltage regulation throughout the power grid. Furthermore, their robust construction and substantial size make them ideal for large-scale applications where both reliability and efficiency are crucial. Thus, they play a vital role in maintaining the smooth operation of extensive power networks.
Auto Transformer
Auto transformers are a variant of three-winding transformers where the primary and secondary windings share a common winding. This design allows for a more compact and cost-effective solution compared to traditional power transformers. Auto transformers are used when a small voltage adjustment is needed, and they offer high efficiency and low impedance. They are commonly employed in applications like voltage regulation in power systems and in certain industrial processes where precise voltage control is essential.